|
Biochemistry of Meiotic Recombination
Analysis of the structural architecture of meiotic recombination complexes
Characterization of the mechanism of homolog bias in meiosis
Role of Rad51 in genome stability and cancer
Small molecule stimulators of Rad51-DNA binding
Rad51 plays key roles in
promoting DNA replication and in repairing DNA double strand
breaks that form spontaneously or by the action of DNA damaging
agents. We study the mechanisms through which Rad51 promotes DNA
repair in human tumor cells. Recently we focused on a hitherto
unappreciated function of Rad51. While Rad51 is best known for its
role in promoting genome stability through DNA repair, our studies
in budding yeast and human cells provided evidence that Rad51 (and
its meiotic counterpart Dmc1) also promote genome
instability. We further found that DNA translocases of
the Rad54 family act to counter this genotoxic activity (Holzen et
al. 2006, Shah et al. 2010, Mason et al. 2015). When the
translocases are depleted, DNA replication and chromosome
segregation are impaired. We are working to determine if and how
the genome destabilizing activity of Rad51 contributes to tumor
progression. We also seek to exploit the genotoxic activity of
Rad51 to target tumor cells during cancer treatment (see project
entitled “Small molecule stimulators of Rad51-DNA
binding”).
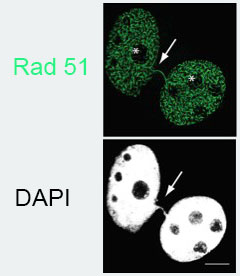
Two partially separated HT1080 human tumor cell nuclei. The cell line was engineered to express very high levels of RAD51 and subject to depletion of DNA translocases RAD54L and RAD54B. Rad51 is in green. Note that in this situation, long filaments of RAD51 form. The results suggest that these filaments are bound to undamaged double stranded DNA (Mason). Note the DNA bridge between the two cells is decorated with RAD51. DAPI is a DNA-specific dye.
Holzen, T. M., Shah, P. P., Olivares, H. A., and Bishop, D. K. (2006) Tid1/Rdh54 Promotes Dissociation of Dmc1 from Non-Recombinogenic Sites on Meiotic Chromatin. Genes Dev. 20, 2593-2604
Shah, P.P., Zheng, X., Epshtein, A., Carey, J.N., Bishop, D.K., and Klein, H.L. (2010) Swi2/Snf2-Related Translocases Prevent Accumulation of Toxic Rad51 Complexes During Mitotic Growth. Mol. Cell 39, 862-872.
Mason, J.M., Dusad, K., Wright, W.D., Grubb, J., Budke, B., Heyer, W.-D., Connell, P.P., Weichselbaum, R.R., and Bishop, D.K. (2015) RAD54 family translocases counter genotoxic effects of RAD51 in human tumor cells. Nucleic Acids Res. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv175
page top
|